|
Whitewater Racing, Whitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that froths, making the water appear opaque and white. The term "whitewater" also has a broader meaning, applying to any river or creek that has a significant number of rapids. The term is also used as an adjective describing boating on such rivers, such as whitewater canoeing or whitewater kayaking. Fast rivers Four factors, separately or in combination, can create rapids: gradient, constriction, obstruction, and flow rate. Gradient, constriction, and obstruction are streambed topography factors and are relatively consistent. Flow rate is dependent upon both seasonal variation in precipitation and snowmelt and upon release rates of upstream dams. Streambed topography Streambed topography is the primary factor in creating rapids, and is generally consistent over time. Increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's Stream gradient, gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that foam, froths, making the water appear opaque and white. The term "whitewater" also has a broader meaning, applying to any river or creek that has a significant number of rapids. The term is also used as an adjective describing boating on such rivers, such as whitewater canoeing or whitewater kayaking. Fast rivers Four factors, separately or in combination, can create rapids: gradient, constriction, obstruction, and flow rate. Gradient, constriction, and obstruction are streambed topography factors and are relatively consistent. Flow rate is dependent upon both seasonal variation in precipitation and snowmelt and upon release rates of upstream dams. Streambed topography Streambed topography is the primary factor in creating rapids, and is generally consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchison Falls
Murchison Falls, also known as Kabalega Falls, is a waterfall in Uganda, located at the apex of Lake Albert on the White Nile. At the top of Murchison Falls, the Nile forces its way through a gap in the rocks, only wide, and tumbles , before flowing westward into Lake Albert. The outlet of Lake Victoria sends around of water over the falls, squeezed into a gorge less than wide. Some historians believe that a party of Roman legionaries dispatched by Nero to explore the Nile may have reached Murchison Falls in 61 AD, but there is major controversy about the feasibility of what would have been a very difficult achievement. Samuel Baker and Florence Baker were the first Europeans who officially sighted the falls. Baker named them after Roderick Murchison, the President of the Royal Geographical Society. The falls lend their name to the surrounding Murchison Falls National Park. During the regime of Idi Amin in the 1970s, the name was changed to Kabalega Falls, after the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youghiogheny River
The Youghiogheny River ( ), or the Yough ( ) for short, is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Monongahela River in West Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania. It drains an area on the west side of the Allegheny Mountains northward into Pennsylvania, providing a small watershed in extreme western Maryland into the tributaries of the Mississippi River. Youghiogheny is a Lenape word meaning "a stream flowing in a contrary direction". Variant names According to the Geographic Names Information System, it has also been known historically as: * Gawgawgamie, Ohio Gani River, Roonanetto, Yanghyanghgain, Yaughvaughani, Yauyougaine River, Yawyawganey, Yawyougaine River, Yeoyogani, Yochio Geni, Yoghioghenny River, Yogyogany River, Yohioganey, Yohogany, Youghiogeny River, Youghogania, Youghyaughye, Youghyoghgyina River, Yoxhio geni River, Yoxhiogany, Yoxhiogeny, Yoxyougaine River, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dike (geology), dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF diagram, QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddy (fluid Dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current (water), current created when the fluid is in a Turbulence, turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object. Fluid behind the obstacle flows into the void creating a swirl of fluid on each edge of the obstacle, followed by a short reverse flow of fluid behind the obstacle flowing upstream, toward the back of the obstacle. This phenomenon is naturally observed behind large emergent rocks in swift-flowing rivers. An eddy is a movement of fluid that deviates from the general flow of the fluid. An example for an eddy is a vortex which produces such deviation. However, there are other types of eddies that are not simple vortices. For example, a Rossby wave is an eddy which is an undulation that is a deviation from mean flow, but does not have the local closed streamlines of a vortex. Swirl and eddies in engineering The propensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
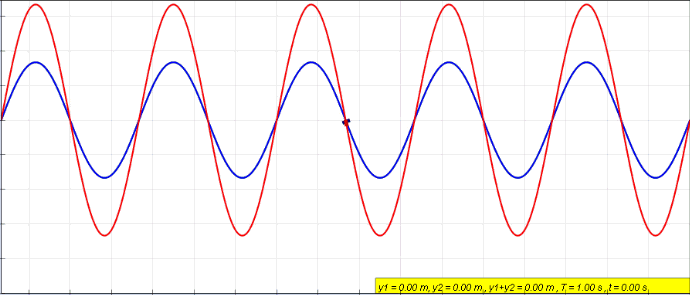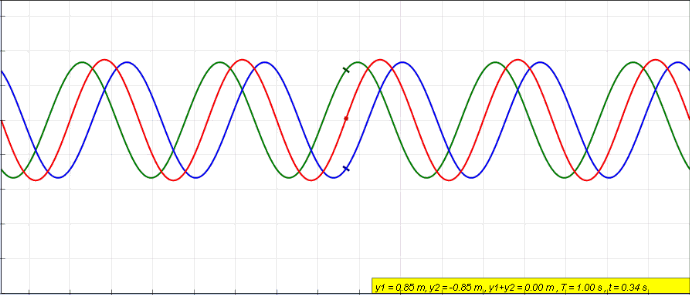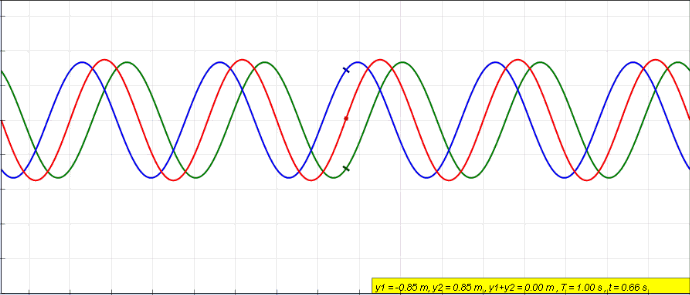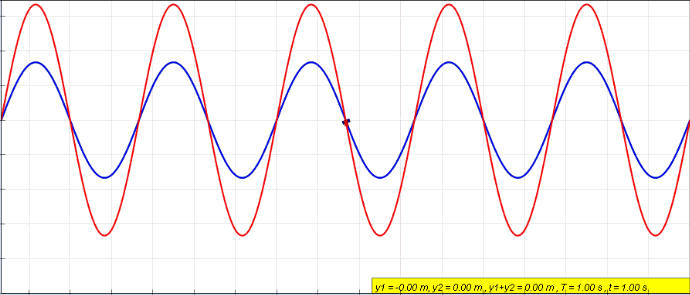
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called node (physics), nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first described scientifically by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed Faraday wave, standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a travelling wave; by contrast, a pair of superposition principle, superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a ''standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. There are two types of waves that are most commonly studied in classical physics: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. In a mechanical wave, Stress (mechanics), stress and Strain (mechanics), strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (physics), deformation (strain) in some physical medium that propa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weir
A weir or low-head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the water level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of lakes, ponds, and reservoirs. There are many weir designs, but commonly water flows freely over the top of the weir crest before cascading down to a lower level. There is no single definition as to what constitutes a weir. ''Weir'' can also refer to the skimmer found in most in-ground swimming pools, which controls the flow of water pulled into the filtering system. Etymology The word likely originated from Middle English ''were'', Old English ''wer'', a derivative of the root of the verb ''werian,'' meaning "to defend, dam". The German cognate is ''Wehr'', which means the same as English weir. Function Commonly, weirs are used to prevent flooding, measure water discharge, and help render rivers more Navigability, navigable by boat. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Playboating
Canoe freestyle (also known as playboating) is a discipline of whitewater kayaking or canoeing where people perform various technical moves in one place (a playspot), as opposed to downriver whitewater kayaking, whitewater canoeing or kayaking where the objective is to travel the length of a section of river (although whitewater paddlers will often stop and play en route). Specialised canoes or kayaks (boats) known as playboats are often used, but any boat can be used for playing. The moves and tricks are often similar to those performed by snowboarders, surfers or skaters, where the athlete completes spins, flips, turns, etc. With modern playboats it is possible to get the kayak and the paddler completely airborne while performing tricks. The competitive side of playboating is known as freestyle kayaking (formerly called rodeo). Playspots Playspots are typically stationary features on rivers, in particular standing waves (which may be breaking or partially breaking), hydraulic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |